Oral Microbial species, Cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease
Why mouth care can support whole body health, in particular your Brain.
It’s a ghastly debilitating and soul destroying condition for both the sufferer and their loved ones.
I’m sure every person reading this has been touched in some way by the scope of Dementia.
I lost my mum, a beautiful vital and vibrant women to rapid onset Vascular dementia. The whole family felt like we lost her twice. A decline so quick it was breathtaking.
My mission is to be across the latest science on this insidious disease and it’s prevention. For me this is not only professionally but personally relevant.
The oral microbiome is now a very hot area for research, not just for OLD folk but for ALL ages.
It is well studied that the Gut microbiome and their bacterial by-products can affect your Brain and your whole body directly and indirectly. Understanding your specific mechanisms can help us guide preventive care.
So… what do we understand so far about whole body impact of your oral bacteria?
Cardiovascular Disease : The link between oral health and heart disease is one of the most well-established connections. People with periodontal disease have a higher risk of experiencing cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes. There are several mechanisms proposed ;
· Oral bacteria like “P gingivalis” have been found in atherosclerotic plaques.
· Inflammatory markers triggered by oral bacteria contribute to arterial inflammation.
· The body’s immune response to oral pathogens may increase blood clotting factors.
Diabetes : The relationship between diabetes and oral health works both ways:
· People with diabetes are more susceptible to periodontal disease due to compromised immunity and blood vessel changes.
· Conversely, periodontal inflammation makes glycemic control more difficult, creating a vicious cycle.
· Treatment of periodontal disease has been shown to improve glycemic control in some diabetic patients.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: The similarities between periodontal disease and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are striking:
· Both involve chronic inflammation and bone destruction.
· P. gingivalis can modify proteins in a way that may trigger autoimmune responses associated with RA.
· RA patients with periodontal disease often see improvement in arthritis symptoms when their oral health improves.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Cognitive Decline: The emerging connection between oral health and neurodegenerative diseases has garnered significant attention …. more to follow
· Oral bacteria have been found in the brains of Alzheimer’s patients.
· P. gingivalis produces enzymes called gingipains that have been linked to neuronal damage.
· Chronic inflammation from periodontal disease may contribute to inflammatory processes in the brain.
Respiratory Infections: The proximity of the mouth to the respiratory tract creates a natural pathway for oral bacteria to affect lung health:
· Aspiration of oral pathogens can contribute to pneumonia, especially in vulnerable populations.
· Periodontal disease has been associated with increased risk and severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Pregnancy Complications: The oral-systemic connection extends to pregnancy outcomes:
· Periodontal disease has been associated with preterm birth and low birth weight.
· Maternal oral bacteria can be transmitted to the fetus, potentially affecting the development of the infant’s microbiome.
As I review your Microbiome results sampled from your lower gut, I am provided a window into your unique population of oral microbes.
Your mouth is home to multiple species of bacteria, including those that can cause periodontal (gum) disease.
These are relevant clinical clues for those, like me with a family history and genetic variants rendering them susceptible to Alzheimer's Disease (AD) and Cognitive decline.
A recent analysis led by NIA scientists suggests that bacteria that cause gum disease are also associated with the development of AD and related dementias, especially vascular dementia.
These results were reported in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Here's a simple step by step look at the proposed connections.
Inflammation: Oral infections and a gut out of balance can trigger whole body inflammation, which may contribute to the development of AD.
Brain Inflammation: Some oral microbes can potentially spread to the brain, causing vascular and tissue inflammation with potential to impact memory and cognitive function.
Amyloid Formation: Some researchers suggest that certain species within the oral microbiome may contribute to the formation of amyloid plaques, a hallmark of AD, through the production of amyloid-like proteins.
Neuroinflammation: is a leading cause of neuronal necrosis and AD pathology. The waste products produced by certain intestinal microorganisms can affect the activity of microglia and further promote neuroinflammation.
Gut-Brain Axis: The interaction between the gut microbiome and the brain, known as the gut-brain axis, is under significant research investigation for its role in AD.
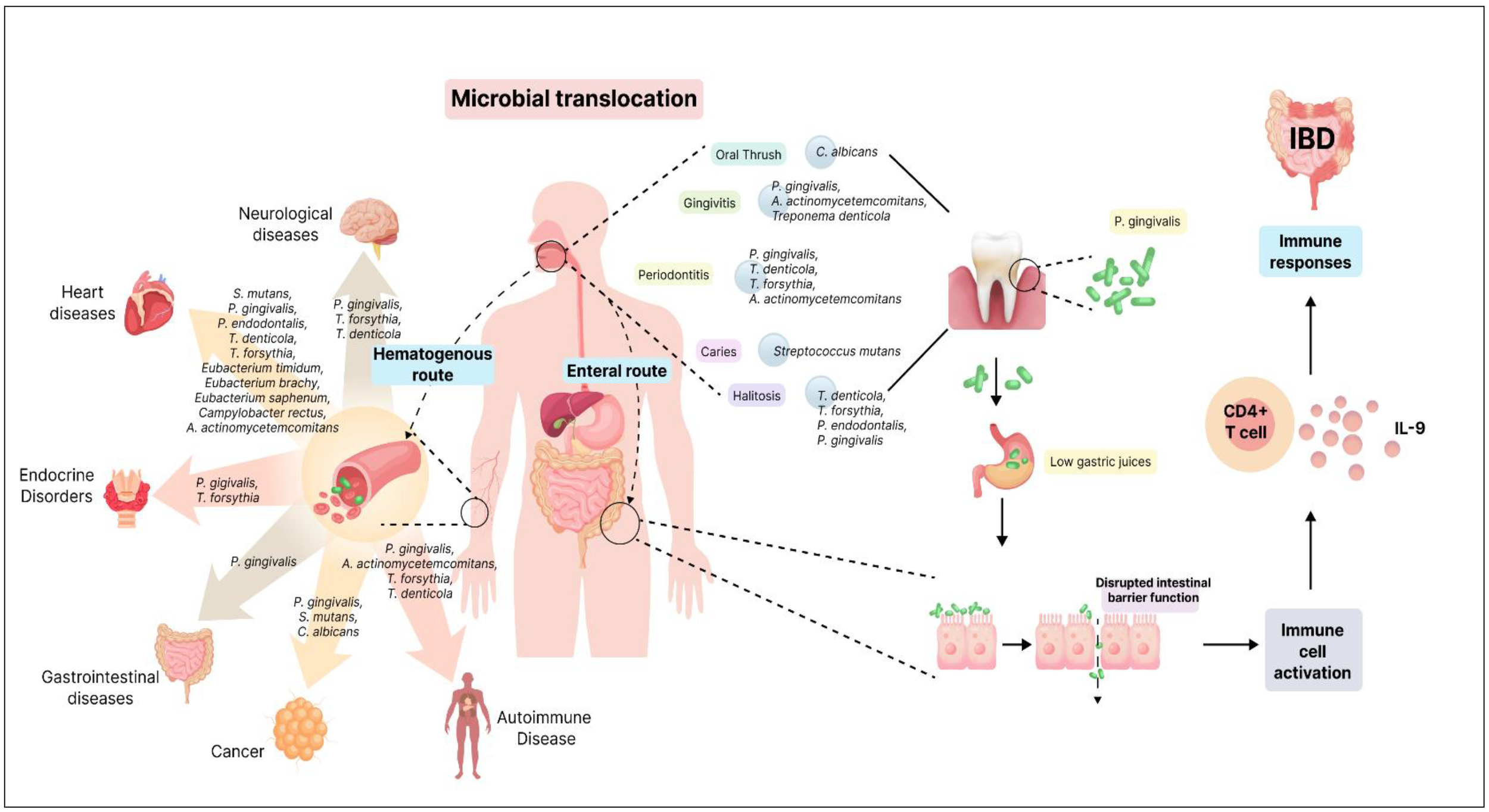
So if the oral bacteria are so closely tied to what happens in the rest of the body, ……. how do they get from the mouth to cause problems in other areas?
The answer is likely in one or all of three routes:
Through the oesophagus – directly moving down to invade the gut.
Through the periodontal blood to enter the systemic circulation of the entire body.
Through the bloodstream as waste products of the oral bacteria – causes the body to exist in a low-grade inflammatory state.
For those who like the detail
Research included > 6000 participants and a 26 year follow up.
The NIA Intramural Research Program team used publicly available national US data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination survey. (NHANES), a large population study performed by the CDC’s National Centre for Health statistics. The team examined whether gum disease and infections with oral bacteria were linked to dementia diagnoses and deaths using Medicare records and the National Death Index.
The team compared different age groups at baseline, with up to 26 years of follow-up, for more than 6,000 participants. The NHANES participants had received a dental exam for signs of gum disease. In addition, the participants received blood tests to measure antibodies against causative bacteria.
The team then analysed antibodies against 19 oral bacteria for an association with the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s, diagnosis of any kind of dementia, and death from Alzheimer’s.
Of these 19 oral bacteria, P gingivalis is the most common culprit of gum disease.
A recent study suggests that plaques of beta amyloid protein, a major hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, may be produced as a response to this infection.
The analysis revealed that older adults with signs of gum disease and mouth infections at baseline were more likely to develop Alzheimer’s during the study period.
Among those 65 years or older, both Alzheimer’s diagnoses and deaths were associated with antibodies against the oral bacterium P. gingivalis, which can cluster with other bacteria such as Campylobacter rectus and Prevotella melaninogenica to further increase those risks.
A long-term follow-up for this study is needed because the findings suggest that oral infection preceded the diagnosis of dementia. After all, having dementia makes it more likely that an individual will not be able to brush and floss effectively, which increases the likelihood of such infections and gum disease. In any case, it is important to keep in mind that population studies can show association but not causality. The authors emphasize that clinical trials are needed to test whether treating infections with P. gingivalis can reduce the development or symptoms of dementia.
My Key Takeaways :
· Good oral care is so much more than a beautiful smile.
· Typically oral bacterial health declines with age as you have less of the healthiest microbes to balance the unhealthy
· Suspicious associations are observational between “P gingivalis” antibodies and the formation of amyloid plaque
· Raised oral species may be related to an unhealthy microbial tract lower down in your gut. Long term use of antacids have been implicated here.
· Raised oral species on your Microbiome testing raises my suspicion and we will be targeting nutritional and lifestyle strategies to balance.
The bright news is that, from my clinical experience, 3-4 months of targeted care has capacity to shift the biome’s populations to a significantly healthier picture.
Suggestions for supporting your oral bacteria
· 6 monthly professional cleans and regular dental checks.
· Don't use astringent mouthwash as it can impair the ecosystem of your healthier oral bacteria.
· eat nitrate rich foods, leafy greens, beetroot.
· limit high glycaemic, processed sugars and ultra-processed foods.
· brush and floss regularly but don't over sterilize.
· stay well hydrated, saliva is your healthy microbiome's ally.
· investigate your intestinal microbiome to support and optimise for whole body health and preventive care.
I am on a mission to educate and empower you and your family.
This information provided does not constitute medical advice nor does it replace a scheduled client consultation and client patient relationship.
References
Oral Microbiome and Alzheimer’s Disease Jason Wan et al. PMCID: PMC10609607 PMID: 37894208Microorganisms 2023 Oct 13;11(10):2550.
2. Clinical and Bacterial Markers of Periodontitis and Their Association with Incident All-Cause and Alzheimer's Disease Dementia in a Large National Survey Beydoun M, et al. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2020;75(1):157-172. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200064.
3. The Oral-Gut-Brain AXIS: The Influence of Microbes in Alzheimer’s Disease
Front. Cell. Neurosci. , 14 April 2021
Sec. Cellular Neuropathology
Volume 15 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.633735